Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (21): 3361-3366.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.21.015
Previous Articles Next Articles
Combination of olfactory ensheathing cells and chitosan in treatment of peripheral nerve injury
Chang Rui, Yin Xiao-long, Shang Bao-sheng, He Peng
- Department of Orthopedics, Hospital of China XD Group, Xi’an 710077, Shaanxi Province, China
-
Online:2014-05-21Published:2014-05-21 -
Contact:Chang Rui, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Hospital of China XD Group, Xi’an 710077, Shaanxi Province, China -
About author:Chang Rui, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Hospital of China XD Group, Xi’an 710077, Shaanxi Province, China -
Supported by:the Project of Shaanxi Provincial Health Bureau in 2012, No. 2012D56
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chang Rui, Yin Xiao-long, Shang Bao-sheng, He Peng . Combination of olfactory ensheathing cells and chitosan in treatment of peripheral nerve injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(21): 3361-3366.
share this article
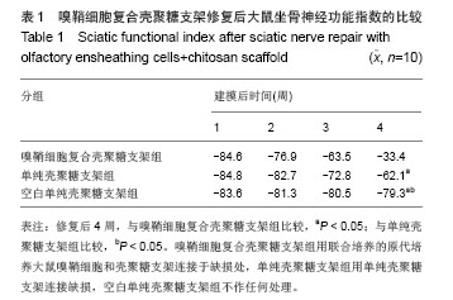
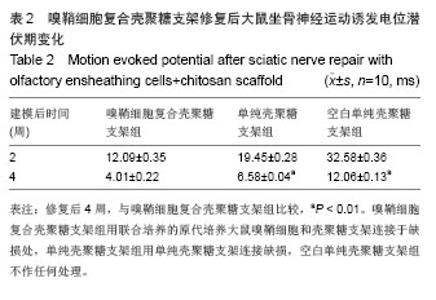
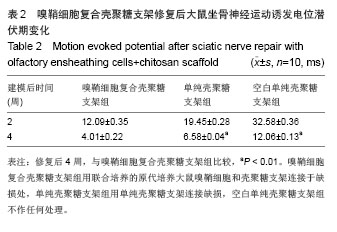
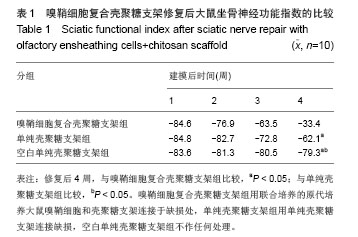
2.3 嗅鞘细胞复合壳聚糖支架修复坐骨神经损伤大鼠一般形态变化 各组大鼠建模后大体观察所有大鼠均正常存活,各组均出现足肿胀,但无足底溃疡、化脓或感染。表明细胞移植不会引起排斥反应,安全良好。建模后1 d,各组SD大鼠患肢足趾弯曲,无法伸展,行走时拖拽,针刺无收缩反应。建模后2周,除空白单纯壳聚糖支架组外,其他2组SD大鼠肌肉萎缩有恢复,行走时拖曳程度降低,针刺能引起微弱的收缩。修复后4周,除空白单纯壳聚糖支架组外,其他2组大鼠肌肉萎缩恢复,僵直消失,其中嗅鞘细胞复合壳聚糖支架组的大鼠足趾有较大握力,存在明显针刺反应。 2.4 嗅鞘细胞复合壳聚糖支架修复后大鼠坐骨神经功能变化 表1显示建模后1-4周各组大鼠坐骨神经指数变化。建模后1周,各组坐骨神经功能指数大致相同,约为-83.6,1周后各组大鼠的坐骨神经功能指数均随时间的延长而提高。修复后4周,嗅鞘细胞复合壳聚糖支架组修复速率最快,3组间坐骨神经功能指数比较均差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。"
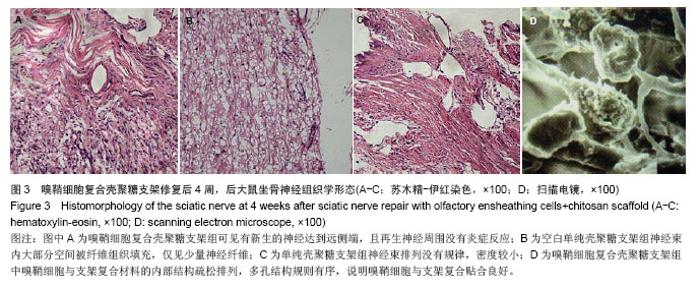
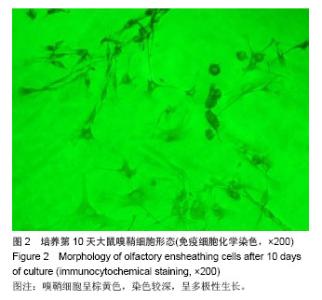
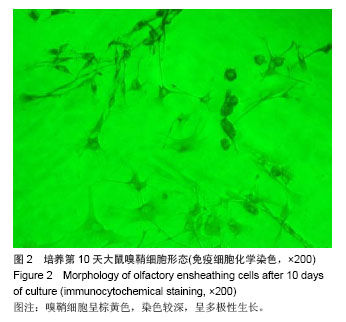
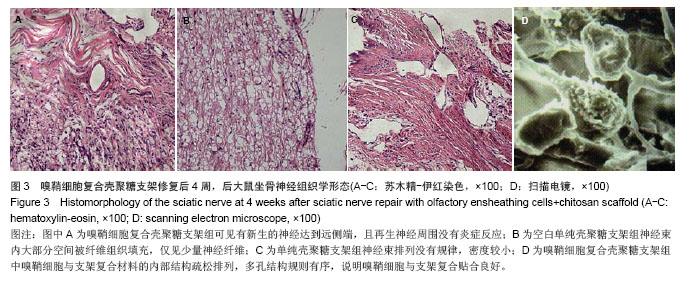
2.6 嗅鞘细胞复合壳聚糖支架修复后大鼠坐骨神经组织学形态 苏木精-伊红染色显示,修复后4周,坐骨神经组织纵切面光学显微镜可见,嗅鞘细胞复合壳聚糖支架组有新生的神经达到远侧端,且再生神经周围没有炎症反应,证明壳聚糖支架具有良好的组织相容性,见图3A。空白单纯壳聚糖支架组神经束内大部分空间被纤维组织填充,仅见少量神经纤维,见图3B。单纯壳聚糖支架组新生神经干数目明显多于空白单纯壳聚糖支架组,但是神经束排列没有规律,密度较小,见图3C。扫描电镜下显示,嗅鞘细胞复合壳聚糖支架组嗅鞘细胞与支架复合情况显示,材料的内部结构疏松排列,多孔结构规则有序,说明嗅鞘细胞与支架复合贴合良好,见图3D。 2.7 移植后生物相容性及不良反应评价 嗅鞘细胞复合壳聚糖支架修复坐骨神经损伤大鼠生物相容性良好,无不良反应发生。"
| [1]Fairless R, Barnett SC. Olfactory ensheathing cells: their role in central nervous system repair. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005; 37(4):693-699. [2]Ramer LM, Au E, Richter MW, et al. Peripheral olfactory ensheathing cells reduce scar and cavity formation and promote regeneration after spinal cord injury. J Comp Neurol. 2004;473(1):1-15. [3]Lee JY, Kim KH, Shin SY, et al. Enhanced bone formation by transforming growth factor- beta1- releasing collagen/ chitosan microgranules. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2006; 76(3): 530- 539. [4]Zhang Y, Cheng X, Wang J, et al. Novel chitosan/collagen scaffold containing transforming growth factor-beta1 DNA for periodontal tissue engineering. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;344(1):362-369. [5]The Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China. Guidance suggestion of caring laboratory animals. 2006-09-30. [6]常瑞,阴小龙.预损伤嗅粘膜对自体嗅鞘细胞体外培养的作用[J].中国组织工程与临床康复,2008,12(51):10001-10004. [7]廖文,刘淑红,张世强,等.壳聚糖导管复合自体骨髓间充质干细胞修复大鼠13 mm坐骨神经缺损[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2007,11(18):3517-3522. [8]Keilhoff G, Goihl A, Stang F, et al. Peripheral nerve tissue engineering: autologous Schwann cells vs transdifferentiated mesenchymal stem cells. Tissue Eng. 2006;12(6):1451-1465. [9]梁楠,张晓,徐艳.神经组织工程细胞外基质材料研究进展[J].西南军医,2006, 8(6):69-72. [10]Leffler CC, Muller BW. Influence of the acid type on the physical and drug liberation properties of chitosan-gelatin sponges. Int J Pharm. 2000;194(2):229-237. [11]Chandy T, Sharma CP. Chitosan-as a biomaterial. Biomat Art Cells Art Org. 1999;18(1):1-24. [12]Takeda Y, Asou H, Murakami Y, et al. A nonneuronal isoform of cell adhesion molecule L1: tissue-specific expression and functional analysis. J Neurochem. 1996;66(6):2338-2349. [13]Schnell L, Fearn S, Klassen H, et al. Acute inflammatory responses to mechanical lesions in the CNS: differences between brain and spinal cord. Eur J Neurosci. 1999;11(10): 3648-3658. [14]Kakulas BA. A review of the neuropathology of human spinal cord injury with emphasis on special features. J Spinal Cord Med. 1999;22(2):119-124. [15]McPhail LT, Stirling DP, Tetzlaff W, et al. The contribution of activated phagocytes and myelin degeneration to axonal retraction/dieback following spinal cord injury. Eur J Neurosci. 2004;20(8):1984-1994. [16]Murthy M, Bocking S, Verginelli F, et al. Transcription factor Runx1 inhibits proliferation and promotes developmental maturation in a selected population of inner olfactory nerve layer olfactory ensheathing cells. Gene. 2014;540(2): 191-200. [17]Botero L, Gomez RM, Chaparro O. Pathogenesis of spinal cord injuries and mechanisms of repair induced by olfactory ensheathing cells. Rev Neurol. 2013;56(10):521-531. [18]Qi F, Wang Y, Ma T, et al. Electrical regulation of olfactory ensheathing cells using conductive polypyrrole/chitosan polymers. Biomaterials. 2013;34(7):1799-809. [19]Campisi A, Spatuzza M, Russo A, et al. Expression of tissue transglutaminase on primary olfactory ensheathing cells cultures exposed to stress conditions. Neurosci Res. 2012; 72(4): 289-295. [20]Tharion G, Indirani K, Durai M, et al. Motor recovery following olfactory ensheathing cell transplantation in rats with spinal cord injury. Neurol India. 2011;59(4):566-572. [21]Simón D, Martín-Bermejo MJ, Gallego-Hernández MT, et al. Expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 by olfactory ensheathing glia promotes axonal regeneration. Glia. 2011; 59(10):1458-1471. [22]Lu ZF, Shen YX, Zhang P, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 promotes proliferation and neurotrophin expression of olfactory ensheathing cells. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2010;12(4): 265-272. [23]Yan HB, Zhang ZM, Jin DD, et al. The repair of acute spinal cord injury in rats by olfactory ensheathing cells graft modified by glia cell line-derived neurotrophic factor gene in combination with the injection of monoclonal antibody IN-1. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2009;47(23):1817-1820. [24]Scott AL, Ramer MS. Schwann cell p75NTR prevents spontaneous sensory reinnervation of the adult spinal cord. Brain. 2010;133(Pt 2):421-432. [25]Pellitteri R, Spatuzza M, Stanzani S, et al. Biomarkers expression in rat olfactory ensheathing cells. Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 2010;2:289-298. [26]Radtke C, Schmitz B, Spies M, et al. Peripheral glial cell differentiation from neurospheres derived from adipose mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2009;27(8): 817-823. [27]Kocsis JD, Lankford KL, Sasaki M, et al. Unique in vivo properties of olfactory ensheathing cells that may contribute to neural repair and protection following spinal cord injury. Neurosci Lett. 2009;456(3):137-142. [28]Runyan SA, Phelps PE. Mouse olfactory ensheathing glia enhance axon outgrowth on a myelin substrate in vitro. Exp Neurol. 2009;216(1):95-104. [29]Bretzner F, Liu J, Currie E, et al. Undesired effects of a combinatorial treatment for spinal cord injury--transplantation of olfactory ensheathing cells and BDNF infusion to the red nucleus. Eur J Neurosci. 2008;28(9):1795-807. [30]Shyu WC, Liu DD, Lin SZ, et al. Implantation of olfactory ensheathing cells promotes neuroplasticity in murine models of stroke. J Clin Invest. 2008;118(7):2482-2495. [31]Guest JD, Herrera L, Margitich I, et al. Xenografts of expanded primate olfactory ensheathing glia support transient behavioral recovery that is independent of serotonergic or corticospinal axonal regeneration in nude rats following spinal cord transection. Exp Neurol. 2008;212(2):261-274. [32]Wu J, Sun TS, Ren JX, et al. Ex vivo non-viral vector-mediated neurotrophin-3 gene transfer to olfactory ensheathing glia: effects on axonal regeneration and functional recovery after implantation in rats with spinal cord injury. Neurosci Bull. 2008;24(2):57-65. [33]Furukawa S, Furukawa Y. FGF-2-treatment improves locomotor function via axonal regeneration in the transected rat spinal cord. Brain Nerve. 2007;59(12):1333-1339. [34]Pellitteri R, Spatuzza M, Russo A, et al. Olfactory ensheathing cells exert a trophic effect on the hypothalamic neurons in vitro. Neurosci Lett. 2007;417(1):24-29. [35]Raisman G, Li Y. Repair of neural pathways by olfactory ensheathing cells. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;8(4):312-319. [36]Pastrana E, Moreno-Flores MT, Avila J, et al. BDNF production by olfactory ensheathing cells contributes to axonal regeneration of cultured adult CNS neurons. Neurochem Int. 2007;50(3):491-498. [37]Cao L, Su Z, Zhou Q, et al. Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor promotes olfactory ensheathing cells migration. Glia. 2006;54(6):536-544. [38]Cui Q. Actions of neurotrophic factors and their signaling pathways in neuronal survival and axonal regeneration. Mol Neurobiol. 2006;33(2):155-179. [39]Marshall CT, Lu C, Winstead W, et al. The therapeutic potential of human olfactory-derived stem cells. Histol Histopathol. 2006;21(6):633-643. [40]Steward O, Sharp K, Selvan G, et al. A re-assessment of the consequences of delayed transplantation of olfactory lamina propria following complete spinal cord transection in rats. Exp Neurol. 2006;198(2):483-499. [41]Kumar R, Hayat S, Felts P, et al. Functional differences and interactions between phenotypic subpopulations of olfactory ensheathing cells in promoting CNS axonal regeneration. Glia. 2005;50(1):12-20. [42]Wewetzer K, Kern N, Ebel C, Radtke C, Brandes G. Phagocytosis of O4+ axonal fragments in vitro by p75- neonatal rat olfactory ensheathing cells. Glia. 2005;49(4): 577-587. [43]Williams SK, Franklin RJ, Barnett SC. Response of olfactory ensheathing cells to the degeneration and regeneration of the peripheral olfactory system and the involvement of the neuregulins. J Comp Neurol. 2004;470(1):50-62. [44]Hendriks WT, Ruitenberg MJ, Blits B, et al. Viral vector-mediated gene transfer of neurotrophins to promote regeneration of the injured spinal cord. Prog Brain Res. 2004; 146:451-476. [45]Woodhall E, West AK, Vickers JC, et al. Olfactory ensheathing cell phenotype following implantation in the lesioned spinal cord. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2003;60(10): 2241-2253. [46]Biers SM, Brading AF. Nerve regeneration: might this be the only solution for functional problems of the urinary tract? Curr Opin Urol. 2003;13(6):495-500. [47]Ruitenberg MJ, Plant GW, Hamers FP, et al. Ex vivo adenoviral vector-mediated neurotrophin gene transfer to olfactory ensheathing glia: effects on rubrospinal tract regeneration, lesion size, and functional recovery after implantation in the injured rat spinal cord. J Neurosci. 2003; 23(18):7045-7058. [48]Lipson AC, Widenfalk J, Lindqvist E, et al. Neurotrophic properties of olfactory ensheathing glia. Exp Neurol. 2003; 180(2):167-171. [49]Shen H, Tang Y, Wu Y, et al. Influences of olfactory ensheathing cells transplantation on axonal regeneration in spinal cord of adult rats. Chin J Traumatol. 2002;5(3): 136-141. [50]Kwon BK, Tetzlaff W. Spinal cord regeneration: from gene to transplants. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(24 Suppl): S13-22. [51]Lacroix S, Tuszynski MH. Neurotrophic factors and gene therapy in spinal cord injury. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2000;14(4):265-275. [52]Nash HH, Borke RC, Anders JJ. New method of purification for establishing primary cultures of ensheathing cells from the adult olfactory bulb. Glia. 2001;34(2):81-87. [53]Woodhall E, West AK, Chuah MI. Cultured olfactory ensheathing cells express nerve growth factor, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, glia cell line-derived neurotrophic factor and their receptors. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2001;88(1-2): 203-213. [54]Fry EJ. Central nervous system regeneration: mission impossible? Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2001;28(4): 253-258. [55]Boruch AV, Conners JJ, Pipitone M, et al. Neurotrophic and migratory properties of an olfactory ensheathing cell line. Glia. 2001;33(3):225-229. [56]Ramón-Cueto A, Nieto-Sampedro M. Regeneration into the spinal cord of transected dorsal root axons is promoted by ensheathing glia transplants. Exp Neurol. 1994;127(2): 232-244. [57]Ramón-Cueto A, Pérez J, Nieto-Sampedro M. In vitro enfolding of olfactory neurites by p75 NGF receptor positive ensheathing cells from adult rat olfactory bulb. Eur J Neurosci. 1993;5(9):1172-1180. |
| [1] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [2] | Gu Xia, Zhao Min, Wang Pingyi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua. Relationship between hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha and hypoxia signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1284-1289. |
| [3] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [4] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [5] | Xie Wenjia, Xia Tianjiao, Zhou Qingyun, Liu Yujia, Gu Xiaoping. Role of microglia-mediated neuronal injury in neurodegenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [6] | Yang Yang, Yao Yu, Shen Xiaotian, Liu Jiajia, Xue Jianhua. Expression and significance of interleukin-21 in intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 690-694. |
| [7] | Ma Binxiang, He Wanqing, Zhou Guangchao, Guan Yonglin. Triptolide improves motor dysfunction in rats following spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 701-706. |
| [8] | Song Shan, Hu Fangyuan, Qiao Jun, Wang Jia, Zhang Shengxiao, Li Xiaofeng. An insight into biomarkers of osteoarthritis synovium based on bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 785-790. |
| [9] | Zhao Xiang, Wei Cuilan, Zhang Yeting. Neurogenesis and neuroinflammation under exercise: alteration and regulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 813-820. |
| [10] | Li Li, Ma Li. Immobilization of lactase on magnetic chitosan microspheres and its effect on enzymatic properties [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 576-581. |
| [11] | Xu Xiaoming, Chen Yan, Song Qian, Yuan Lu, Gu Jiaming, Zhang Lijuan, Geng Jie, Dong Jian. Human placenta derived mesenchymal stem cell gel promotes the healing of radiation skin damage in SD rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3976-3980. |
| [12] | Li Xinping, Cui Qiuju, Zeng Shuguang, Ran Gaoying, Zhang Zhaoqiang, Liu Xianwen, Fang Wei, Xu Shuaimei. Effect of modification of β-tricalcium phosphate/chitosan hydrogel on growth and mineralization of dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3493-3499. |
| [13] | Bi Qingwei, Liu Chengpu, Li Yan, Zhao Wenwen, Han Mei. Structure analysis of platelet-rich fibrin derived from two centrifugation procedures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3534-3539. |
| [14] | Cui Tiantian, Yi Lan, Ouyang Hougan, Wu Huiting, Ouyang Yanchu, Chen Chu. Effect of thermosensitive moxibustion in a rat model of pelvic inflammation based on trifocal focal membrane theory [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3168-3172. |
| [15] | Song Shilei, Chen Yueping, Zhang Xiaoyun, Li Shibin, Lai Yu, Zhou Yi. Potential molecular mechanism of Wuling powder in treating osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3185-3193. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||